High Volume Data Management
This documentation covers best practices and procedures for managing high volumes of attendance data generated by biometric/time attendance devices.
System Requirements
Hardware Requirements:
- Server: Minimum 8-core CPU, 32GB RAM, RAID 10 storage configuration
- Storage: SSD storage recommended (minimum 500GB for 1,000+ employees)
- Network: Gigabit Ethernet with dedicated VLAN for attendance devices
Software Requirements:
- Database: MySQL 8.0+ or Microsoft SQL Server 2019+
- Recommended: Columnar database for analytics (e.g., ClickHouse, Amazon Redshift)
- Middleware: Message queue system (RabbitMQ, Apache Kafka) for data ingestion
Data Architecture
Optimal Database Schema:
CREATE TABLE attendance_records ( record_id BIGINT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, device_id VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, employee_id VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, timestamp DATETIME(6) NOT NULL, verification_mode TINYINT, -- 1=Fingerprint, 2=Face, 3=Card, etc. status TINYINT, -- 0=Invalid, 1=Valid, 2=Duplicate raw_data BLOB, -- Optional biometric template data INDEX idx_employee (employee_id), INDEX idx_timestamp (timestamp), INDEX idx_device (device_id) ) ENGINE=InnoDB PARTITION BY RANGE (YEAR(timestamp)*100 + MONTH(timestamp)) ( PARTITION p202301 VALUES LESS THAN (202302), PARTITION p202302 VALUES LESS THAN (202303), -- ... additional partitions );
Data Processing Pipeline
-
Ingestion Layer:
- Device Database
- Batch processing for offline device synchronization
- Real-time stream processing for live devices
-
Processing Workflow:
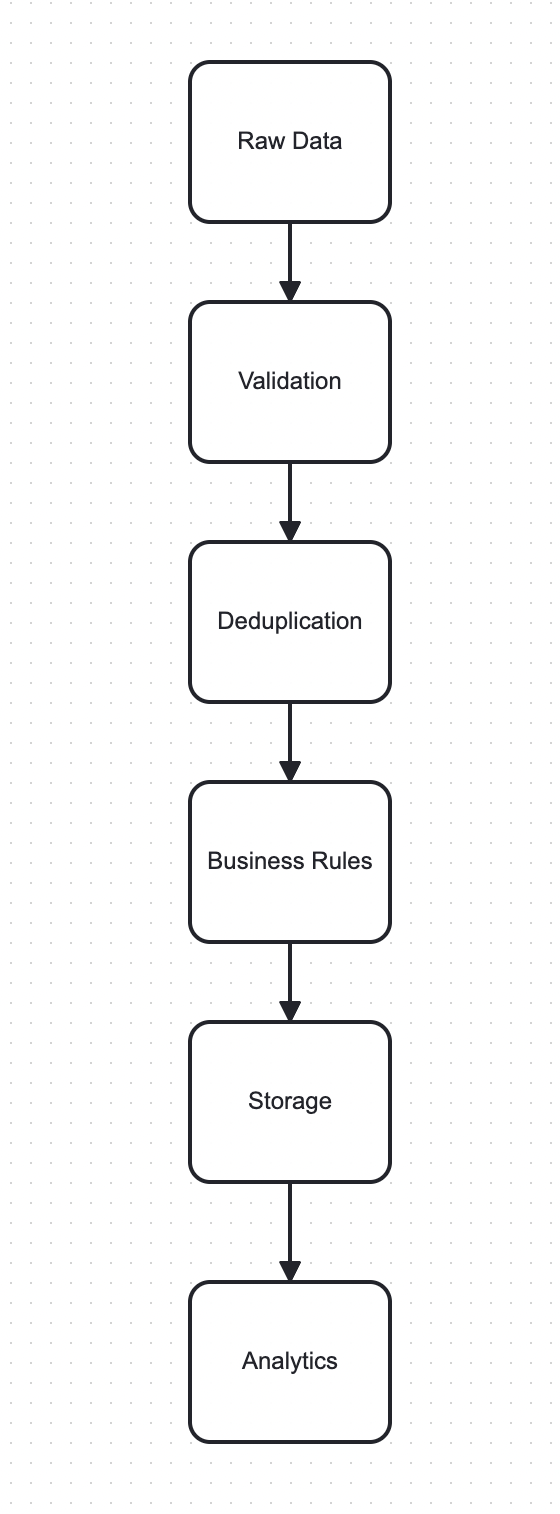
(No steps were included here in original input)
Performance Optimization
Database Optimization
- Implement monthly partitioning for attendance tables
- Use columnar storage for analytics queries
- Configure appropriate indexes (avoid over-indexing)
- Implement database sharding for multi-location deployments
Application Optimization
- Implement data compression for network transmission
- Use connection pooling for database access
- Cache frequently accessed data (employee lists, device configs)
- Implement read replicas for reporting queries
Backup Strategy
- Full Backups: Weekly compressed backups to offsite location
- Incremental Backups: Daily differential backups
- Disaster Recovery: Hot standby in alternate location with 15-minute RPO
Monitoring and Maintenance
Key Metrics to Monitor
- Records processed per minute
- Database query latency
- Storage growth rate
- Device synchronization success rate
Maintenance Tasks
- Monthly index reorganization
- Quarterly partition maintenance
- Annual storage capacity planning
- Regular performance tuning
Scaling Considerations
Vertical Scaling
- Upgrade server resources (CPU, RAM, storage)
- Implement faster storage (NVMe SSDs)
Horizontal Scaling
- Database read replicas
- Microservices architecture for processing
- Distributed file storage for biometric data