Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a security framework that restricts system access to authorized users based on their assigned roles. In PrismERP, RBAC is the foundational mechanism to manage who can access different features, data modules, and system functionalities. Roles represent a collection of permissions that govern user capabilities, and they simplify user management by grouping permissions together rather than assigning them individually.
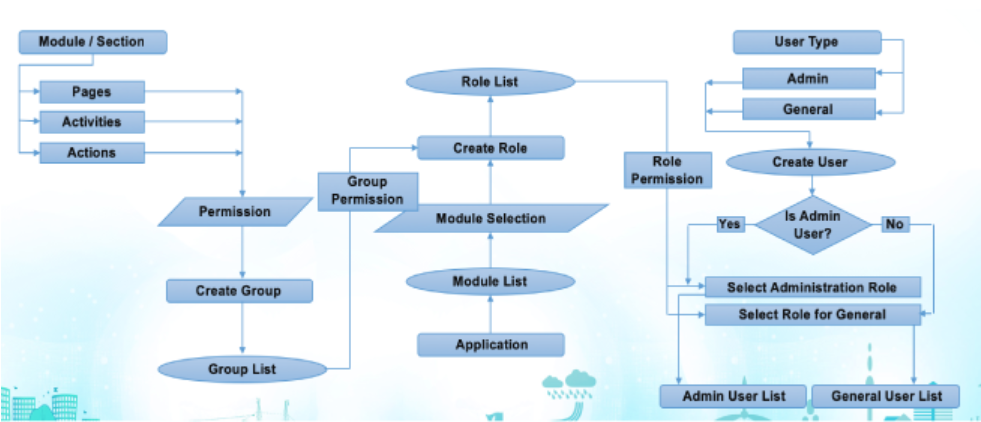
Key Features of RBAC
-
Centralized Role Definition: Roles are defined centrally and consist of permissions that correspond to system actions or resources.
-
User Assignment: Users are assigned one or more roles, implicitly granting them the permissions associated with those roles.
-
Granular Permission Control: Permissions can include access to specific modules, menus, reports, and data entities.
-
Hierarchical Roles and Inheritance: Roles can be structured hierarchically, allowing more senior or admin roles to inherit permissions from basic roles.
-
Audit Trail and Compliance: RBAC supports tracking of role assignments and permission changes for governance and audits.
-
Dynamic Modification: Roles and permissions can be updated as organizational needs evolve, allowing flexible access control.
Use Role-Based Access Control
-
Enhanced Security: Restricts access strictly to what is needed for an individual’s job, reducing risk of unauthorized data access.
-
Simplified User Management: Instead of managing individual permissions, admins assign roles that encapsulate access rights.
-
Operational Efficiency: Quickly onboard users by assigning predefined roles fitting their job function.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Helps demonstrate control over sensitive data access and user permissions.
-
Adaptability: Easily accommodates changes in organization structure by updating roles.
-
Clear Accountability: Assigning roles makes it easier to track who has access to what, supporting audits and security reviews.
RBAC is Used in PrismERP
-
Access Role Management: Admins navigate to the User Access Control section under Administration or General Configuration.
-
Create Roles: Define roles that represent job functions or access requirements.
-
Assign Permissions: Link permissions (access to modules, reports, menus) to roles carefully according to policy.
-
Create and Manage Users: Add users into the system and assign one or more roles.
-
Control User-Role Assignments: Adjust assignments as necessary for organizational changes.
-
Review and Audit: Periodically review roles, permissions, and user-role assignments to maintain security hygiene.
-
Use Additional Security Features: Leverage multi-factor authentication and IP restrictions integrated with RBAC for enhanced protection.
This grouping clearly positions Role-Based Access Control as the overarching security model, with User Management, Role Management, and Role Group Management defined as critical operational components under it. The approach aligns with PrismERP documentation and best practices for enterprise ERP systems.