Bank
The PrismERP Bank feature offers a complete solution for managing banks, bank branches, and EMI charges efficiently. It allows users to add new banks, update branch details, and configure EMI charges with ease. With advanced search, filter, and reporting options, PrismERP ensures accurate tracking of all bank-related information. This module streamlines banking operations and keeps financial records organized and accessible.
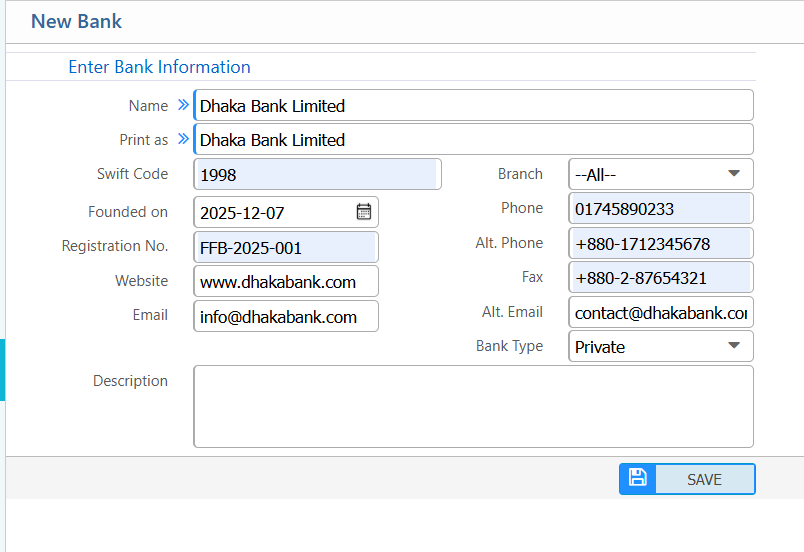
1. Add New Bank
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Enter the bank’s full name. |
| Print As | Specify how the bank name will appear in print documents. |
| Swift Code | Enter the bank’s SWIFT code. |
| Branch | Select the branch. |
| Founded On | Enter the bank’s founding date. |
| Registration No. | Enter the bank’s registration number. |
| Website | Enter the bank’s website URL. |
| Enter the bank’s primary email address. | |
| Phone | Enter the bank’s phone number. |
| Alt. Phone | Enter an alternative phone number. |
| Fax | Enter the bank’s fax number. |
| Alt. Email | Enter an alternative email address. |
| Bank Type | Select the type of bank. |
| Description | Add any additional notes about the bank. |
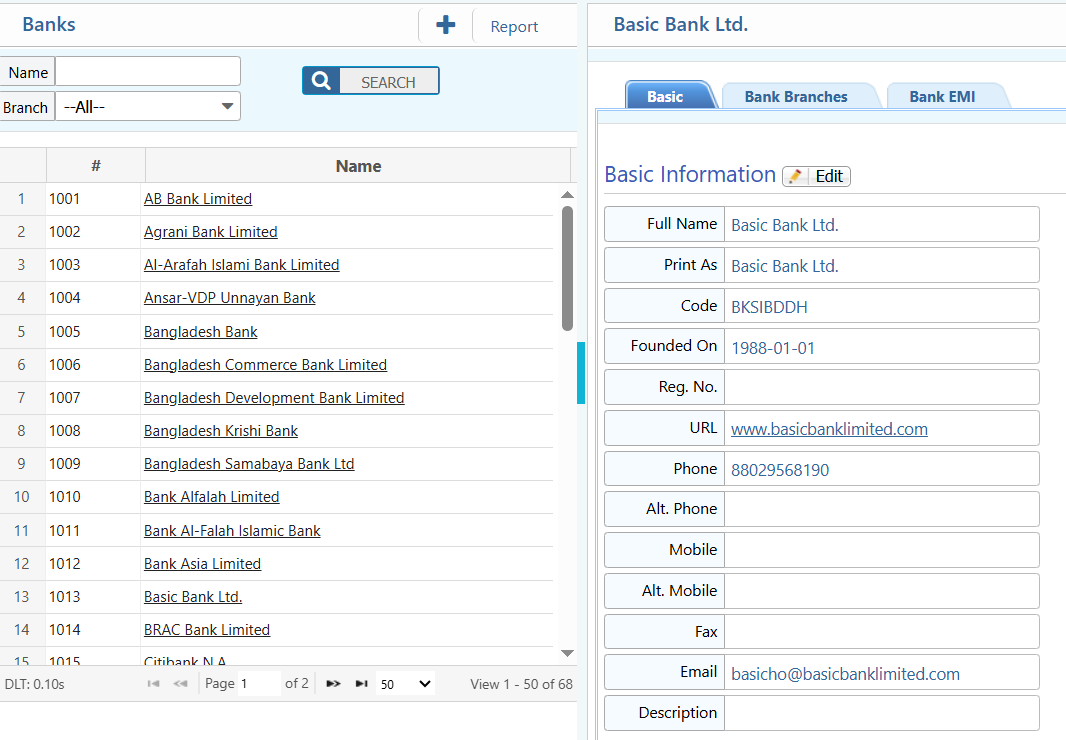
2. List of Bank
2.1 Bank Search & Filter Options
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Search banks by full or partial bank name. |
| Branch | Select a specific branch. |
| Banks Report | Preview and download reports in different formats |
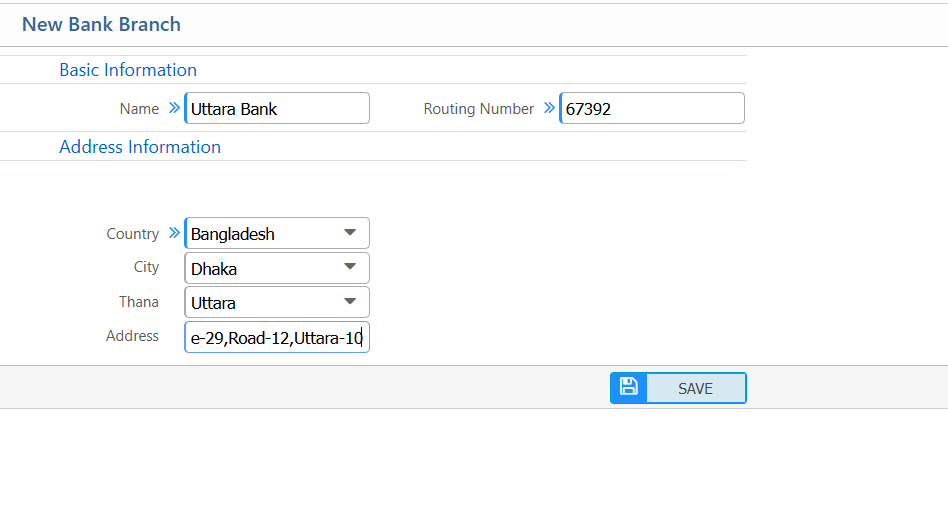
2.2 Add Bank Branch
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Enter the branch name. |
| Routing Number | Enter the branch routing number. |
| Country | Select the country where the branch is located. |
| City | Enter the city of the branch. |
| Thana | Enter the thana of the branch. |
| Address | Enter the full address of the branch. |
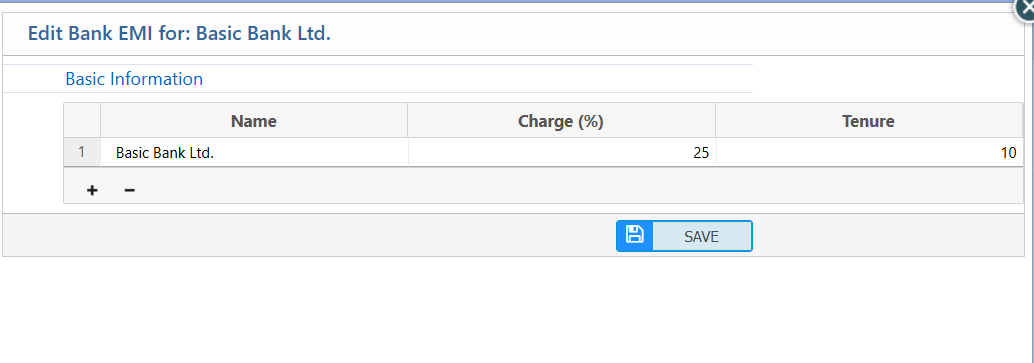
2.3 Update Bank EMI charge
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Select or review the bank name for which the EMI is being edited. |
| Charge (%) | Enter the EMI charge percentage applied by the bank. |
| Tenure | Specify the EMI tenure (in months or years) for the selected bank. |